
Corneobiology and corneotherapy
Corneobiology refers to experimental studies that are focused on the anatomy and biolology of the stratum corneum, the most superficial layer of the skin…

Male skin is decidedly different from that of females and therefore requires specially tailored skincare. What is the difference between male and female skin? The major differences lay in the thickness of the skin, as well as the size and activity of the sebaceous glands of the face.
The actions of male hormones also influence the composition of the skin’s surface, working to stimulate the production of sebum (1). Sebum, consisting mainly of triglycerides and fatty acids, creates a protective film on the skin’s surface, preventing excessive water loss from the upper cell layers. As a result, the skin remains supple and doesn’t dry out.
The elevated amount of sebum, however, creates an environment conducive to the proliferation of higher concentrations of bacteria. In addition, pores can become clogged and subsequently inflamed. One can therefore conclude that men’s skincare should not contain products that are fatty, also termed comedogenic.
Male skin contains more collagen and therefore has increased viscoelasticity and tension. In addition, the collagen fibers are arranged perpendicularly, whereas the fibers are arranged parallel to each other in women.
In one study, the University of Hamburg was able to demonstrate that women up to 50 years of age lost more moisture through their skin when compared to men (2). As a result, male skin ages somewhat more slowly. Nevertheless, men should still practice routine skincare.
An important point in the context of male skincare is the practice of shaving. A man’s beard zone can contain between 5,000 and 30,000 individual hairs. Shaving can irritate the skin and cause microinjuries which can become inflamed. If the horny layer is especially thick, hairs can become ingrown. Routine use of peeling can help prevent this occurrence.
Age is another important factor in the physiology of the skin of both sexes. A 2014 study demonstrated that both the pH of the skin as well as the moisture content of the stratum corneum, the uppermost cell layer, changes with age. The production of sebum by sebaceous glands, however, remains constant (3).
no matter if young or old, man or woman, oily skin type or not – all of us need skincare tailored to our individual needs.

Corneobiology and corneotherapy
Corneobiology refers to experimental studies that are focused on the anatomy and biolology of the stratum corneum, the most superficial layer of the skin…

Nowadays, almost everyone uses a hydrating cream daily. But which daily routine is the best one?
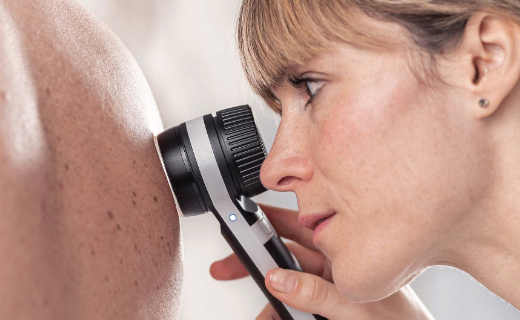
Dermatoscopy of nevus cell nevi
With the aid of a dermatoscope, a so-called reflected-light microscope, skin lesions can be magnified and viewed…
1. Zouboulis CC. The human skin as a hormone target and an endocrine gland. Hormones. 2004;3:9–26.
2. Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M.: Skin physiology in men and women: in vivo evaluation of 300 people including TEWL, SC hydration, sebum content and skin surface pH. Int J Socmet Sci 2013 Oct;35
3. Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M. Age-related changes in male skin: quantitative evaluation of one hundred and fifty male subjects. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27(1):9-17


Erfahre als Erster von Neuigkeiten in der ästhetischen Medizin und profitiere von exklusiven Angeboten sowie Tipps von unseren erfahrenen Dozenten.

We will call you back soon