Abnehmen durch Injektionslipolyse?
Die Injektionslipoyse ist eine beliebte Behandlung in der ästhetischen Medizin, welche zur gezielten Beseitigung kleiner bis mittlerer Fettpölsterchen angewandt…

Hyperhidrosis is a non-physiological increased sweat production, which can be generalized or localized. Localized hyperhidrosis often affects the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, armpits or the head, especially the forehead area.
A distinction is made between the primary, i.e. congenital hyperhidrosis and the secondary form, which is the result of a disease. The primary form typically manifests itself in childhood or adolescence. The hyperhidrosis usually manifests itself focally in one or more areas with a bilateral, symmetrical picture and occurs at least once a week.
The secondary form, on the other hand, may be the result of hormonal causes, hyperthyroidism, hypopituitarism, drugs, hypoglycaemia, chronic infections, malignancies, obesity, or psychological problems.
For orientation, hyperhidrosis can be divided into three degrees of severity on the palms of the hands and feet as well as the armpits. Mild hyperhidrosis is manifested by sweat patches of 5-10 cm in diameter, moderately severe hyperhidrosis is manifested by sweat patches of 10-20 cm in diameter and in the most severe form the sweat patches have a diameter of more than 20 cm.
Several test methods are available as part of the diagnostic process. The best-known test is the iodine-strength test, also known as the minor test. Here, coloured demarcations of the affected areas of the body are generated using a special iodine solution.
The sweating skin area is first carefully dried and then brushed with iodine. After the area has dried, it is dusted with starch powder. A blue-black colour appears on areas with excessive sweating.
The sympathetic nerves regulate the amount of perspiration, with acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter of the nervous system, transmitting the impulses to the sweat glands. This is where botulinum toxin works to stop increased sweating. Botulinum toxin is a neurotoxin that temporarily blocks the transmission of messenger substances in the nerves.
This occurs due to the strong binding of botulinum toxin to the nerve endings, blocking them and thus preventing the transmission of impulses to the muscle fibers. As a result, the transmission of nerve impulses to the sweat glands is blocked for about 3-6 months. Sweat formation is thus almost completely suppressed.
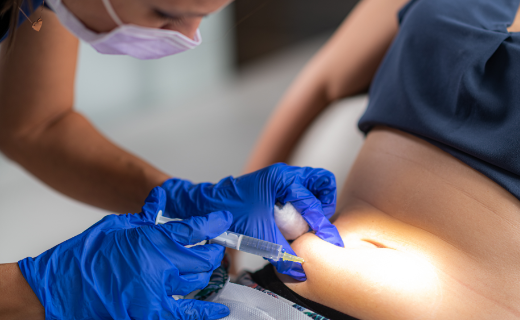
Botulinum toxin is injected into the affected area with a very fine needle. Several points of the area to be treated are punctured. The introduction of the botulinum toxin may cause a slight pain due to tension and puncture pain. The stitch itself is hardly visible afterwards.
The occurrence of minor bleeding or redness around the injection site is possible, as with any other local injection. In some cases, there are small bruises. The result can be observed after about 3-7 days and lasts for up to 6 months.
The only approved preparation in Germany for the treatment of the armpits is Botox®. The treatment of the hands, feet and other localizations is done in the so-called Off Label Use. This means that approved drugs are used for an unapproved indication. It should therefore only be used if it is justified and medically necessary.
Treatment with botulinum toxin can cause side effects, such as small bruises or an increase in sweating in other areas. Furthermore, mostly temporary, but also permanent functional disturbances of nerves such as insensitivity and sensory disturbances may occur.

Abnehmen durch Injektionslipolyse?
Die Injektionslipoyse ist eine beliebte Behandlung in der ästhetischen Medizin, welche zur gezielten Beseitigung kleiner bis mittlerer Fettpölsterchen angewandt…

Antioxidants aid in the prevention of the development of chronic diseases. Common examples include compounds derived specifically from plants…

Ärztliches Honorar in der Ästhetik
Da es sich bei ästhetischen Behandlungen ausschließlich um Privatleistungen handelt, sind diese auch für die behandelnden Ärzte durchaus profitabel. Doch was ver…

We will call you back soon